Receding Gums Causes and Treatment
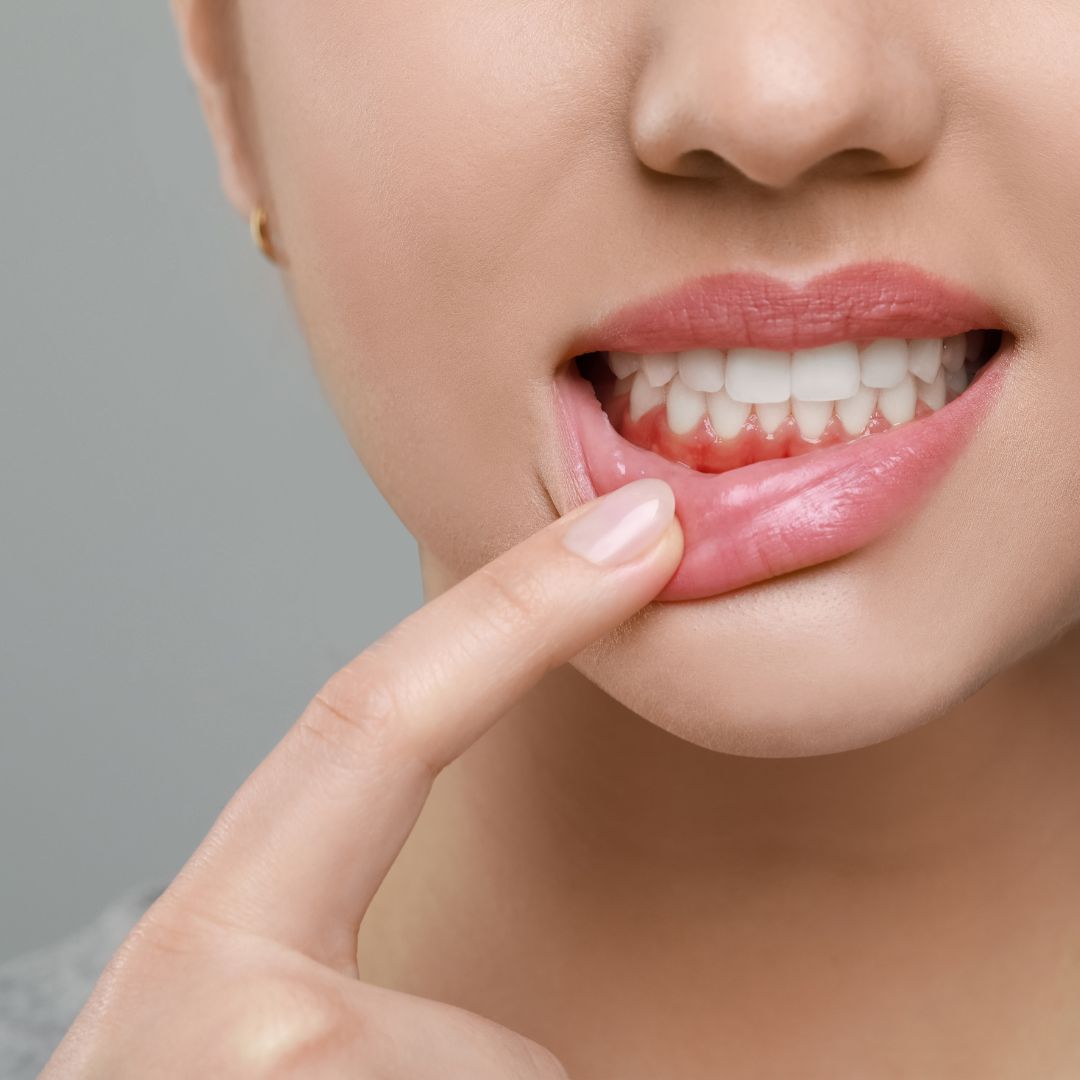

Ever run your tongue along your teeth and notice they seem longer than before? That uncomfortable sensation might be your first clue that your gums are retreating from their natural position. I’ve been there—that moment when you realize something’s not quite right in your mouth can be unsettling.
Receding gums is a common dental concern that affects millions of Americans, often creeping up so gradually you might not notice until it’s advanced. Whether you’re just noticing some sensitivity or you’re actively researching treatment options, you’re in the right place to understand what’s happening and what you can do about it.
What Are Receding Gums?
Gum recession occurs when your gum tissue pulls back from your teeth, exposing more of the tooth or even the tooth’s root. That pink tissue that normally hugs your teeth starts to withdraw, creating pockets or gaps between your teeth and gum line where bacteria can collect.
The technical term for this condition is “gingival recession,” and it’s more than just a cosmetic issue. When gums recede, they leave teeth vulnerable to decay, infection, and eventual loss if left untreated.

What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Receding Gums?
One question I hear frequently in my practice is about the connection between nutrition and gum health. Vitamin deficiencies can indeed play a significant role in gum recession.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Your Gums
Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining healthy gum tissue. When your body lacks sufficient B12, you may experience:
- Inflammation of the gums
- Increased susceptibility to infection
- Delayed healing of gum tissue
- Overall weakened oral health
Does low B12 affect your gums? Absolutely. Studies have shown that vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to periodontal disease, which is a major cause of gum recession. Your body needs B12 to produce healthy red blood cells that carry oxygen to your gum tissue, keeping it robust and resilient.
What does a B12 deficiency tongue look like?
A B12-deficient tongue often appears smooth, shiny, and inflamed—a condition called glossitis. You might notice:
- A bright red, swollen tongue
- Loss of papillae (the tiny bumps on your tongue)
- A burning sensation
- Changes in taste perception
These oral symptoms can appear alongside gum recession, serving as warning signs of nutritional deficiencies that need addressing.
.
Other Vitamin Deficiencies Affecting Gum Health
Vitamin C deficiency can lead to bleeding gums and increased recession risk, while vitamin D deficiency impacts bone density, including the jawbone that supports your teeth and gums.
Which food is rich in vitamin B12? To boost your B12 levels naturally, include these foods in your diet:
- Beef and liver
- Clams and other shellfish
- Fish (especially salmon and trout)
- Eggs
- Dairy products
- Fortified nutritional yeast
For vegans and vegetarians, B12 supplements may be necessary to maintain optimal gum health.
What Is the Most Common Cause of Receding Gums?
While nutritional deficiencies contribute to gum recession, they’re not the primary cause. The most common reasons for receding gums include:

How Do You Fix Receding Gums?
If you’re noticing signs of gum recession, don’t panic—there are numerous treatment options available depending on the severity of your condition.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Does salt water help receding gums? Salt water rinses can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria, making them a helpful supportive treatment. While they won’t reverse recession, regular warm salt water rinses (1 teaspoon salt in 8 ounces of warm water) can support gum health during recovery.
What gel helps your gums grow back? Products containing hyaluronic acid have shown promise for supporting gum tissue regeneration. Some dental gels formulated specifically for gum health contain a combination of herbs, hyaluronic acid, and other compounds that can reduce inflammation and support healing.
Does gum repair gel work? While these products can help with symptoms and support overall gum health, they typically can’t reverse significant recession on their own. Think of them as part of a comprehensive treatment plan rather than a standalone solution.
Professional Dental Treatments
For more advanced recession, professional interventions may be necessary:
Scaling and Root Planing
This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline and smooths the exposed root surfaces to prevent bacteria accumulation.
Gum Grafting
For severe recession, tissue grafting may be necessary to replace lost gum tissue:
- Connective tissue grafts: Tissue is taken from the roof of your mouth and attached to the existing gum tissue.
- Free gingival grafts: Similar to connective tissue grafts but used when more tissue is needed.
- Pedicle grafts: Nearby gum tissue is stretched to cover the recession.
How much does a gum graft cost in the UK? While we’re focusing on treatments in Turkey, it’s worth noting that in the UK, gum grafting procedures typically cost between £600-£1,200 per tooth. This high cost is one reason many Americans and Europeans consider treatment abroad.
Pinhole Surgical Technique
A minimally invasive alternative to traditional grafting, this procedure involves creating small holes in the gum tissue and using special instruments to gently loosen and reposition the gumline.
Receding Gums Treatment in Turkey
Turkey has emerged as a leading destination for dental tourism, offering high-quality gum recession treatments at a fraction of US costs. Many dental clinics in Istanbul, Antalya, and other major cities cater specifically to international patients seeking affordable care.
Why Choose Turkey for Gum Recession Treatment?
- Cost savings: Treatments like gum grafting can cost 50-70% less than in the United States
- Advanced technology: Many Turkish dental clinics boast state-of-the-art equipment and facilities
- Highly trained specialists: Turkish periodontists often receive training internationally
- Comprehensive care packages: Many clinics offer packages including accommodation and transportation
- Opportunity to combine treatment with vacation: Recover while experiencing Turkey’s rich culture and history
Popular Gum Recession Treatments in Turkey
What is the new treatment for receding gums? Turkish dental clinics offer several innovative approaches:
Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Treatment
This cutting-edge treatment uses components of your own blood to accelerate healing after gum procedures. The platelet-rich fibrin contains growth factors that stimulate tissue regeneration and can enhance the results of traditional grafting procedures.
Laser Gum Treatment
Minimally invasive laser therapy can treat mild to moderate recession by removing inflamed tissue and bacteria while stimulating gum regeneration.
AlloDerm Regenerative Tissue Matrix
This donor tissue graft eliminates the need to harvest tissue from your own palate, reducing pain and recovery time while providing excellent results for covering exposed roots.
Treatment Process in Turkey
- Initial consultation: Often conducted virtually before travel
- Treatment planning: Detailed plan and cost estimate provided
- Travel and accommodation: Many clinics assist with logistics
- Treatment phase: Typically 5-7 days depending on complexity
- Follow-up care: Instructions for continuing care after returning home
